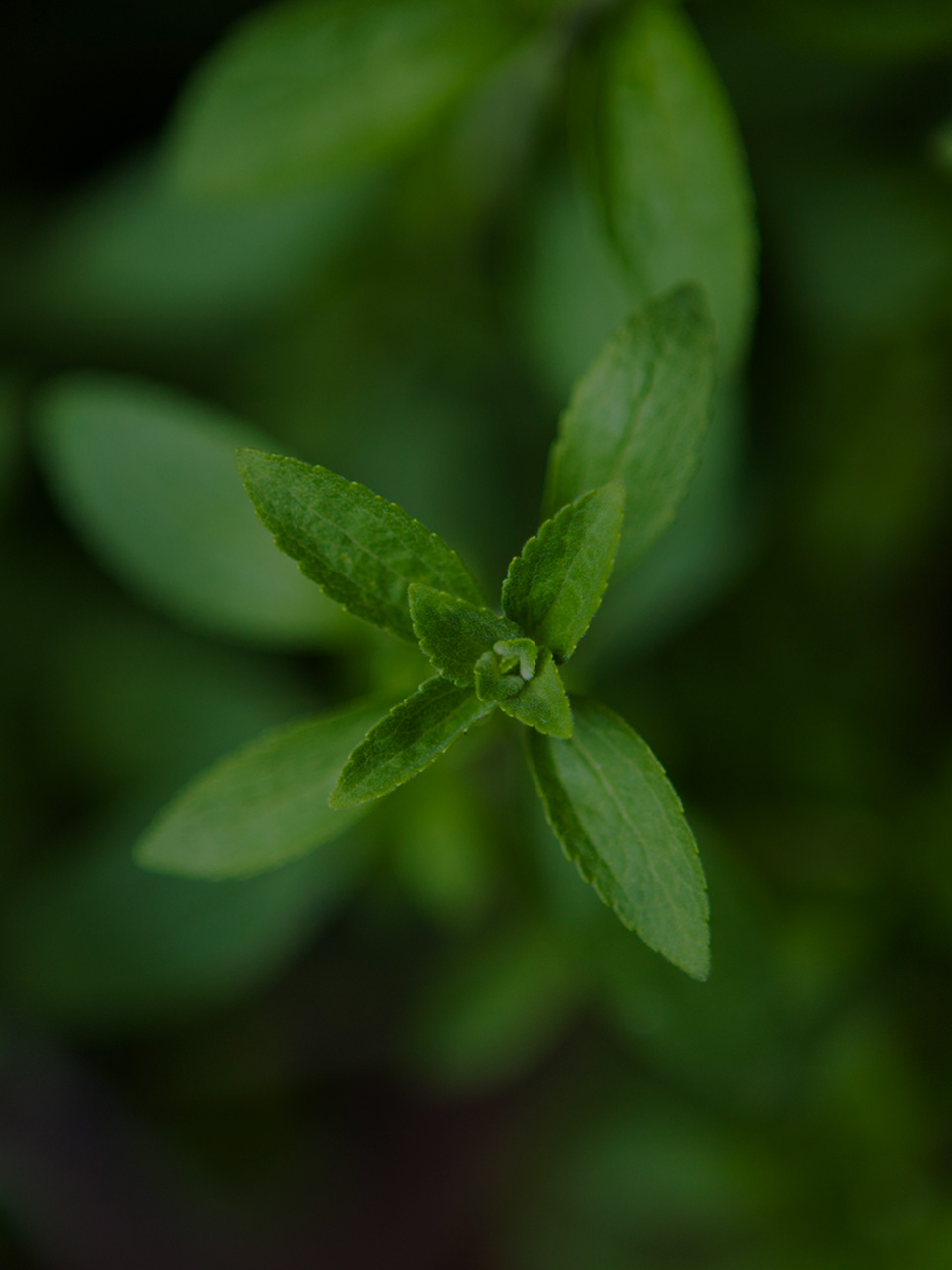
The leaves of the stevia plant have been used as a sweetening agent since ages. Besides its use as a natural sweetener, stevia can help lower blood glucose levels. Enlisted here are the uses of the stevia plant.

Tap to Read ➤
Stevia Plant Uses
Ningthoujam Sandhyarani


The leaves of the stevia plant have been used as a sweetening agent since ages. Besides its use as a natural sweetener, stevia can help lower blood glucose levels. Enlisted here are the uses of the stevia plant.

The genus Stevia belongs to Asteraceae family. It comprises about 240 plant species. Out of these, Stevia rebaudiana is quite popular due to its therapeutic properties. Also referred to as sweet leaf, sugarleaf, or sugar plant, this herb is native to the tropical and subtropical regions of South America. Today, these plants are cultivated all over the world.

Stevia is a perennial plant that thrives in well-drained soils. It grows like a shrub, growing up to a height of about four feet. For mass cultivation, its seeds are sown after the danger of frost has passed. The plantlets grow better in soil temperatures of about 50 to 60 degrees Fahrenheit.

Due to its high sugar content, this plant possesses natural insect-repelling characteristics. Considering this, it is easy to maintain and harvest these plants.

Stevia Plant Extracts
Commercially, stevia leaves are used for making extracts. The leaves are harvested during cold climates (prior to frost), so that more sugar gets accumulated in the leaves. If frost is expected, the plants should be covered with plastic sheets. The harvested leaves are sun-dried first in specific conditions with proper air circulation.

Dried leaves are then processed for extraction of the liquid extracts. These extracts are about 300 times sweeter than the normal table sugar.

Uses

The sweetness of this plant is attributed to the presence of two compounds called stevioside and rebaudioside (Reb A). Hence, for mass cultivation, it is important to select varieties that have high stevioside content. It also contains vitamin C, potassium, magnesium, and niacin.
Sweetener
Stevia sweeteners are readily available in the market. With a glycemic index and nearly zero calorie, they are healthier alternatives to sugar and other artificial sweeteners. They are also used in the preparation of processed foods such as ice-cream, beverages, and other food items.

Tea Leaves
Fresh leaves can be directly used in tea and coffee. However, fresh leaves are required in larger amounts in order to get the desired sweet taste than the dried powder or liquid extract. The fresh leaves impart an earthy taste to tea or coffee.

Homemade Stevia Extract and Powder
Those who grow this plant can use its leaves for making the stevia extract or powder, both of which can be used in various recipes. Liquid extract is prepared by adding hot water in ground leaves, while the powder is made by grinding dried leaves in a food processor.

For Diabetics
For diabetics and other people who are very concerned about their sugar intake, stevia is a healthy sweetening agent. Unlike table sugar, it does not affect or raise the blood sugar level. Hence, diabetics can consume sweet beverages and food items that have been prepared by using the extract or powder.

For Dental Care
Though the leaves taste sweet, these don't cause cavities. In fact, these might help improve dental health. Stevia-based mouthwashes and toothpastes can be used for keeping the gums and teeth healthy.

For Skin and Hair Care
This plant contains antioxidants and phytonutrients, which help keep the skin soft and supple. It also possesses anti-microbial properties. Stevia-based hair products can help in reducing dandruff.

For Wound Healing
Since stevia has antibacterial and antiviral properties, application of fresh leaves or extracts can help heal cuts and wounds. However, make sure that the leaves are washed thoroughly, before you apply them on the affected area.

Though the uses and health benefits of stevia are numerous, crude or whole-leaf stevia has not been approved for use as a food additive by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration). Also, excessive use could cause upset stomach, nausea, or bloating in some individuals.

Those who are allergic to ragweed could develop an allergic reaction to stevia. So, consult your healthcare provider on experiencing any adverse effects.

Disclaimer: The information provided here is solely for educating the reader. It is not intended to be a substitute for the advice of a medical expert.