
Tap to Read ➤
Ginger Root Side Effects
Sonia Nair


Ginger root, popular for its unique flavor and health benefits, has some side effects too. Ginger root side effects are less common, but cannot be ignored.

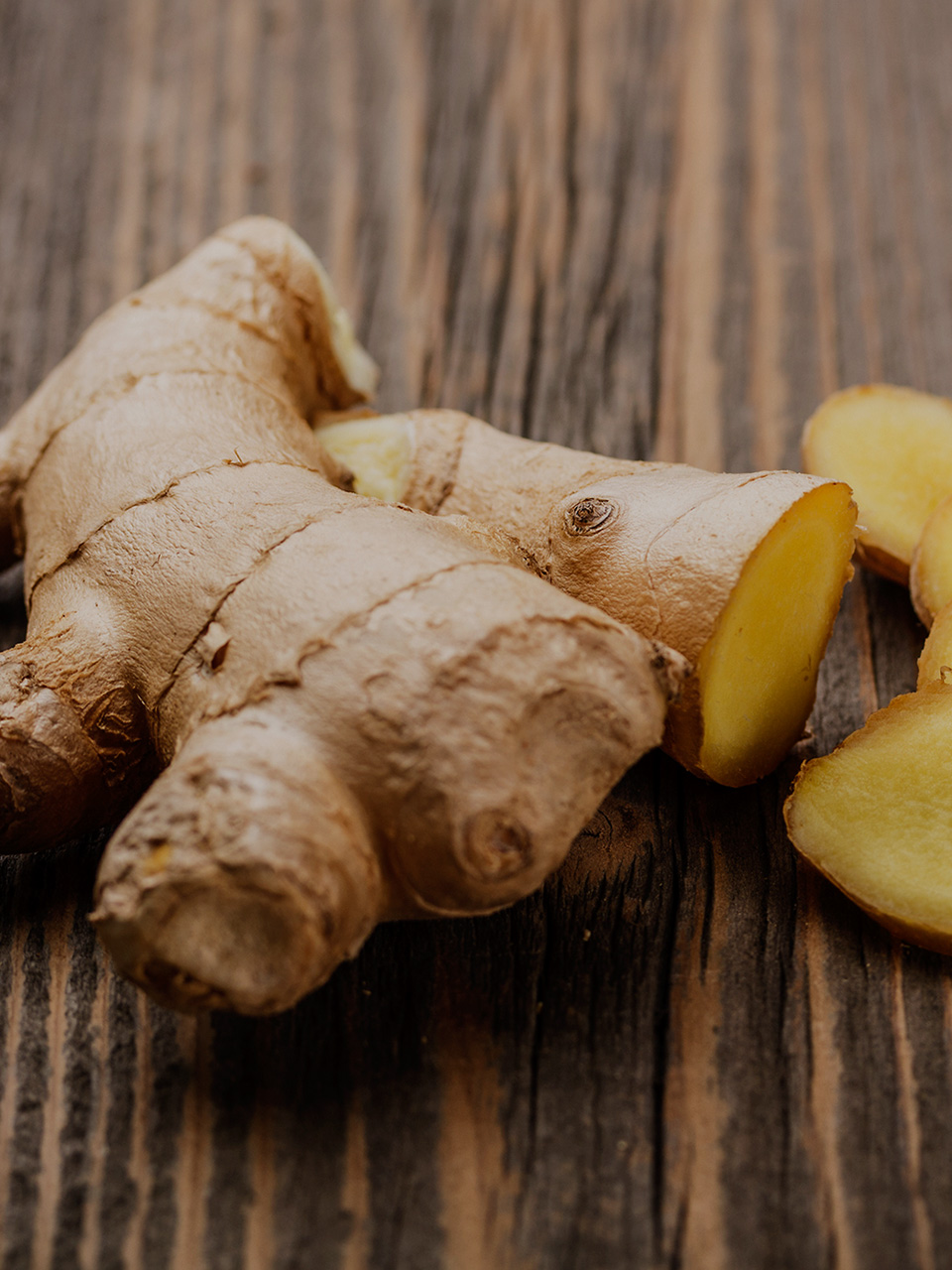
Ginger, otherwise known as ginger root, is native to some parts of Asia like, China and India. The term 'ginger' is used to denote the edible rhizome of the plant Zingiber officinale, which belongs to the family Zingiberaceae, along with turmeric and cardamom. Ginger is very popular across the globe, as a herb as well as a spice.

It is believed that ginger has been used in ancient Chinese and Indian medicine, for treating various medical conditions like cold, cough, diarrhea, indigestion and rheumatism. The medicinal properties of ginger have been mentioned in the writings of the Chinese scholar Confucius and in the ancient Ayurvedic texts of India. From Asia, this herb found its way to Rome and other European countries and is now widely used across the globe.

Medicinal Value of Ginger
As mentioned above, ginger is one of those herbs that has been used for therapeutic purposes, for a very long time. It has been used for treating cold, cough, digestive disorders, menstrual cramps and various other health problems. This herb is believed to possess aphrodisiac powers and is also mentioned in 'Kama Sutra'.
Ginger is used to relieve motion sickness and morning sickness. It has anti-inflammatory properties and is used to relieve pain and inflammation associated with arthritis, rheumatism and muscle cramps.

Ginger is said to be useful for expelling phlegm accumulated in the lungs and so, is found to be effective in treating respiratory diseases like asthma and bronchitis.

It can stimulate blood circulation and is also useful in removing toxins from the body. This herb has blood-thinning and cholesterol-lowering properties, which are beneficial for lowering the risk of heart diseases. Ginger root health benefits are believed to be due to its active components like, gingerols, zingibain, bisabolenel, oleoresins, starch, mucilage and essential oils (zingiberene, zingiberole, camphene, cineol, borneol).

Side Effects
- The most common among ginger root side effects are heartburn, diarrhea and irritation of the mouth.
- In some people, prolonged use of ginger root may lead to dry and scaly rash, which develop initially on the face.
- Another ginger root side effect, associated with its long-term use is visual sensitivity to bright light.
- Ginger root consumption is not recommended for people with gallstones, as this herb increases bile production.

- Ginger should be avoided by those, who take blood-thinning medication. Even those who are preparing for surgery must avoid having ginger in any form.
- Those who are taking medication for diabetes and high blood pressure must not take ginger.
- Ginger should not be consumed by people with bleeding disorders, ulcers and inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Pregnant women are asked to avoid ginger, as this herb may cause uterine contractions. Nursing mothers must also seek expert opinion, before taking ginger.
- It has also been noticed that some people with allergies, develop side effects like skin rash.
- In some rare cases, eye irritation and pink eye have also been associated with consumption of ginger.
- There are also reports, which suggest that ginger might affect blood pressure and heart rhythms.

In short, ginger is a safe herb that is widely used for culinary as well medicinal purposes. Though rare, ginger root side effects may develop in some people. In most cases, such side effects are associated with intake of ginger powder, prolonged use of ginger root or its overuse. Ginger is not found to cause any side effect, if taken in low doses.
Ginger may also interact with other drugs, herbs or supplements and create complications. Hence, it is very important to seek the opinion of your doctor before using this herb for medicinal purposes. Such herbal treatment must be taken under the supervision of a qualified herbal practitioner.
Disclaimer: This story is for informational purposes only and should not be used as a replacement for expert medical advice.